“Thyroid disease” is a term used to describe a set of potentially debilitating conditions involving a disruption in the functioning of the thyroid gland. The thyroid is a butterfly shaped gland located in the front of the neck that is responsible for regulating metabolism, producing and controlling the body’s sensitivity to a wide range of hormones, and managing protein synthesis. When thyroid gland functioning is impaired, the consequences can range from mildly irritating to pervasively disruptive. By overseeing energy functioning within the cells, the thyroid has a profound influence over every aspect of the human body, including the hearth, skin, hair, bones, brain, bowels, and overall mood. Some common types of thyroid disease include goiters (a sometimes visible enlargement of the thyroid gland), hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid), hypothyroidism (an under-active thyroid), thyroid cancer, thyroid nodules (small lumps and growths on the thyroid gland), and thyroiditis (acute or chronic swelling of the thyroid gland).
With well over 20 million Americans currently suffering from some form of thyroid disease, the condition is actually quite common. While almost anyone can develop thyroid disease, individuals fitting one or more of the following descriptions are at an increased risk:
- Women over the age of 60
- Individuals with a preexisting autoimmune disorder
- Individuals with close family member that has been diagnosed with an autoimmune disease
- You have been recently treated with radioactive iodine or received radiation treatment
- Patients who have undergone a previous thyroid procedure or partial thyroidectomy
- Have been pregnant or given birth with in the last 6 – 8 months
If one or more of the thyroid disease risk factors listed above describes you, consult a physician or eye doctor as soon as possible to determine if you have or may be at risk for developing a thyroid condition. Early detection of thyroid dysfunction can help your doctor devise an effective treatment plan and prevent the worsening of any related symptoms.
Signs and Symptoms of Thyroid Disease
The thyroid regulates and produces a number of hormones that control functioning throughout almost every part of the human body. Given its extensive influence, the signs and symptoms related to thyroid gland dysfunction can vary widely in both type and severity. Because the presentation of symptoms can vary so widely and are often non-specific, it is relatively common for up to 5 years to lapse between the onset of thyroid disease and a proper diagnosis. In fact, the signs and symptoms of thyroid disease are often mistaken for depression or irritable bowel syndrome. Some of the most commonly reported symptoms of thyroid disease include:
- Chronic irritability and anxiety
- A rapid or erratic heartbeat
- Unexplained, often sudden weight loss or weight gain
- High blood pressure and/or cholesterol
- Diarrhea, stomachaches, or constipation
- Extreme fatigue
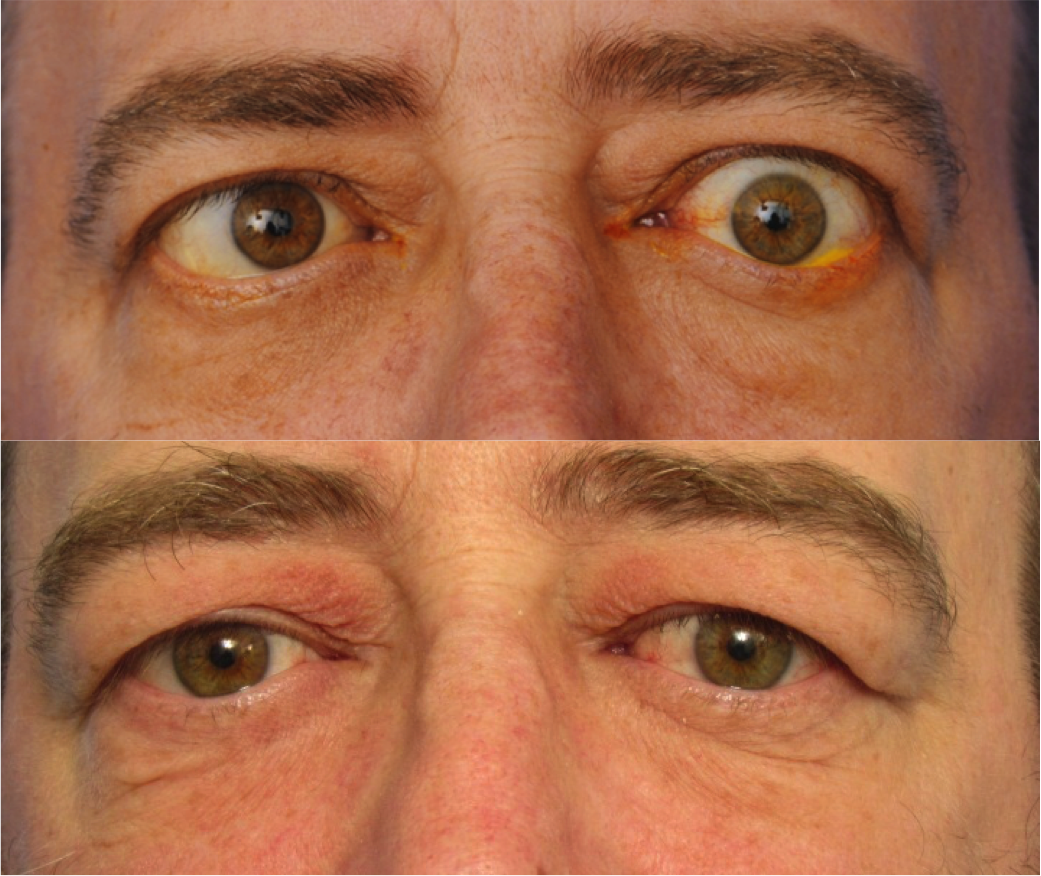
- Thyroid eye disease, or Graves’ disease
- Osteoporosis in some advanced cases
You’re at Risk for Thyroid Disease, What’s Next?
The current available treatments for thyroid disease are safe and incredibly effective. Some of the many custom treatment options available include various medications, a full or partial thyroidectomy. For the thyroid eye disease, orbital decompression may be necessary. To determine which treatment option will be the most effective for your thyroid condition, be sure to schedule a one-on-one consultation with your physician before symptoms worsen or cause any permanent damage.